Serving as interfaces between the real world and electronic systems, sensors convert physical quantities into electrical signals that can be processed, analysed, and utilised for various applications. The importance of sensors in these fields cannot be overstated, as they enable automation, control, and data acquisition in a wide range of industries and applications. And within the consistently growing field of the Internet of Things (IoT) technology, the sensor is a pivotal component.
Growing IoT adoption
There are currently 15 billion connected devices worldwide, which equates to almost two devices per person. According to Statista, the amount of connected devices are predicted to double to almost 30 billion by 2030 with the global population remaining around the 8 million mark, meaning the number of connected devices per person is also predicted to double.
What makes a device smart?
The IoT is considered ‘the third wave’ of IT, after the Internet and mobile communications. To support this intelligent wave, smart devices require three fundamental components.
- Physical. They must have mechanical and electrical parts
- Smart. They must contain items such as sensors, microprocessors, and data storage
- Connected. They must be able to connect, either wired or wireless, with the product via their ports, antennas, or protocols
To make the IoT device a smart device, the ‘thing’ must be able to gather and analyse data which can then automatically perform intelligent actions based on the aforementioned analysis, with little or no human involvement.
Why are sensors important?
According to the ‘IoT Sensors Market 2022 – 2027’ report, IoT sensors now make up a third of all shipped sensors in 2022, with the top five market places for this evolving technology being in: smarter sensors, more power-efficient sensors, soft and virtual sensors, sensor fusion, and biosensors.
These small, intelligent devices are continually evolving, enabling people to gather data, make informed decisions, and create more efficient and sustainable systems – in short, advancing IoT sensor technologies are having a huge impact on our world.
As engineering evolves and technology becomes smarter, innocuous everyday devices such as lights, radios, kitchen appliances, and vehicles are now connected to the Internet via embedded devices, making it possible to connect people and ‘things.’
Aymeric Nicolas, Marketing and Business Development Manager, Position Sensing, Texas Instruments, told Electronic Specifier: “Sensors and IoT are indissociable from one another. IoT hardware collects environmental data that is then transmitted to the network where its analysed and applied. Innovation in sensors is therefore essential in the development of accurate and reliable IoT devices.
“Sensing technology is integral to lower cost and environmentally conscious IoT development. So, it’s important that providers of sensors used in IoT invest in four key areas of innovation: power, size, performance, and integration. Technology, such as low current consumption magnetic sensors, small bottom facing light sensors, high accuracy temperature and humidity sensors, and highly integrated power monitoring sensors are driving changes in the IoT market.”
What is a sensor?
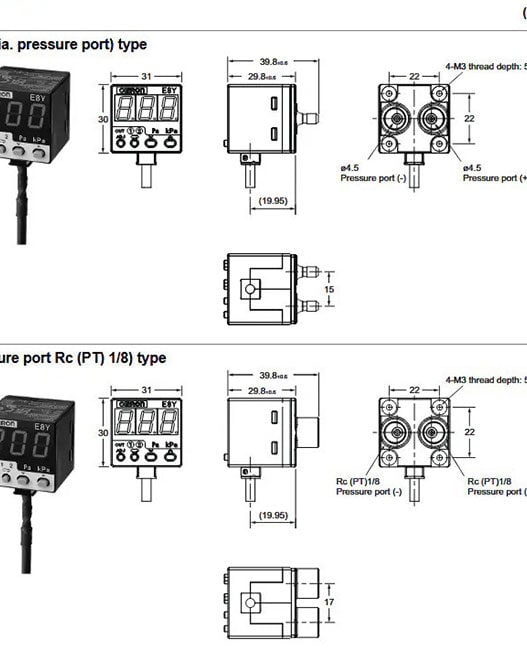
A sensor is a device or component that detects or measures a physical quantity or environmental parameter and converts it into an electrical signal or data that can be used for monitoring, control, analysis, or further processing. Its input can be anything from light, heat, pressure, moisture, and motion to any number of physical phenomena. The output is usually a signal that is converted to a human-readable display at the sensor location or transmitted electronically over a network for reading or further processing.
A sensor’s role within whatever field it is being used in is to be an interface between the physical world and digital systems.
How does a sensor work?
Creating a sensor involves designing and assembling various components to measure a specific physical property.
- Smarter sensors: these sensors can process data locally and make decisions based on that data. This can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted and processed elsewhere, which can save power and reduce latency.
- More power-efficient sensors: these sensors can reduce the amount of power they consume by using techniques such as duty cycling (turning off when not needed), reducing the sampling rate, or using lower-power wireless protocols.
- Soft and virtual sensors: these sensors can be created using software and machine learning algorithms. They can be used to estimate physical quantities that are difficult or expensive to measure directly.
- Sensor fusion: this involves combining data from multiple sensors to get a more complete picture of what’s happening. For example, combining data from an accelerometer and a gyroscope can give you a better estimate of orientation than either sensor alone.
- Biosensors: these sensors can detect biological signals such as heart rate, blood pressure, or glucose levels. They can be used for health monitoring or medical diagnosis.
Sensors: impact on industry and consumer
Commenting on the impact the advancement of sensors in IoT adoption, Nicolas said: “Advancements in sensing technology are not only essential to improving the overall consumer experience while using IoT devices, but also necessary to optimise efficiency and safety in industrial processes driven by real-time data. Power efficiency reduces the need for frequent battery swapping or recharging, which can be difficult to implement at a large scale. Smaller size and greater integration allow more features in a smaller form-factor, enabling smarter systems. Higher performance sensors facilitate more precise movement, reduce latency, and provide more accurate detection of the physical environment. This performance and reliability driven by sensing technology provides the consumer a greater experience using IoT products.”
The advancements in IoT sensor technologies are driving the expansion of the IoT ecosystem, transforming industries, and changing our daily lives. Miniaturisation, energy efficiency, connectivity, sensor fusion, and AI integration are among the key drivers propelling the IoT forward. As sensors continue to evolve, we can anticipate an even smarter, more connected world where data-driven decisions become the norm.