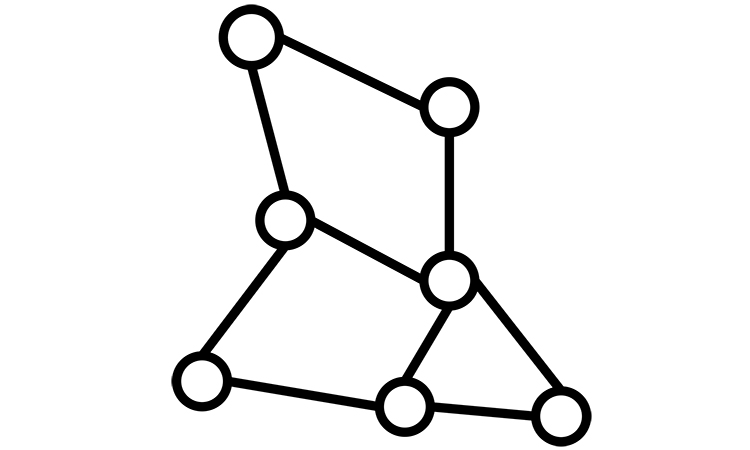
Let us consider the circuit analysis method, using a tree structure. For example, we take a tree of the graph and arbitrary link. They construct a closed loop and assign first loop current.
We can apply the second Law of Kirchhoff to this loop. Let us take a second link, construct a closed loop with a tree, assign a second loop current, and apply the second Law of Kirchhoff to this loop. As there are links, we will get equations. If there are current sources in a graph we should put them on a link, and voltage sources on a branch. This is a common rule for both methods – general nodal and loop analysis. As any voltage can’t be assigned to the current sources, the loop with this source should be discarded.
Example – to resolve general nodal analysis.
We see that both methods give similar results. However, loop analysis takes less equations to find the branch voltages.