Keysight Technologies, Inc. announced the release of Quantum System Analysis, a breakthrough Electronic Design Automation (EDA) solution that enables quantum engineers to simulate and optimise quantum systems at the system level. This new capability marks a significant expansion of Keysight’s Quantum EDA portfolio, which includes Quantum Layout, QuantumPro EM, and Quantum Circuit Simulation. This announcement comes at a pivotal moment for the field, especially following the 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics, which recognised advances in superconducting quantum circuits – a core area of focus for Keysight’s new solution.
System-level quantum analysis has long been a challenge due to the complexity of integrating diverse physical domains – electromagnetic, circuit, and quantum dynamics – into a unified simulation environment. Traditional approaches often rely on fragmented tools and repeated cryogenic experiments, which are both time-consuming and costly. Keysight’s Quantum System Analysis bridges this gap by providing a cohesive platform that enables early validation of quantum system designs, reducing development cycles and improving design confidence.
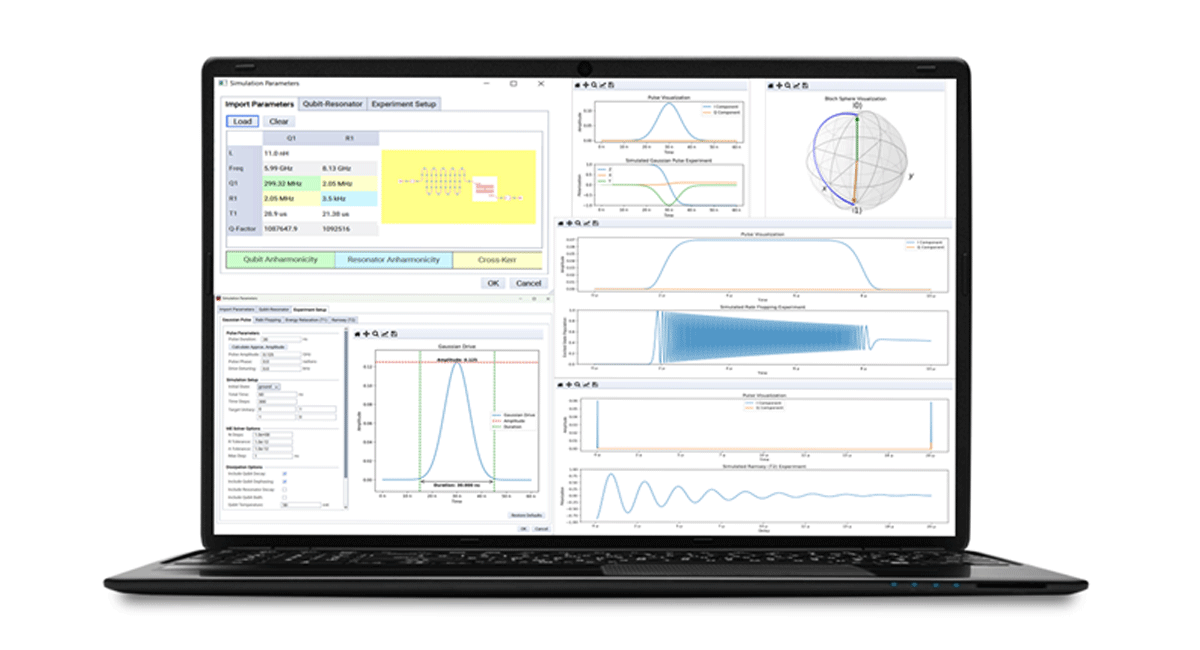
Quantum System Analysis empowers researchers to simulate the quantum workflow, from initial design stages to system-level experiments, reducing reliance on costly cryogenic testing and accelerating time-to-validation. This integrated approach supports simulations of quantum experiments and includes tools to optimise dilution fridge input lines for thermal noise and qubit temperature estimation.
Quantum System Analysis introduces two transformative features:
- Time Dynamics Simulator: Models the time evolution of quantum systems using Hamiltonians derived from electromagnetic or circuit simulations. This enables accurate simulation of quantum experiments such as Rabi and Ramsey pulsing, helping researchers understand qubit behaviour over time.
- Dilution Fridge Input Line Designer: Allows precise modelling of cryostat input lines to qubits, enabling thermal noise analysis and effective qubit temperature estimation. By simulating the fridge’s input architecture, engineers can minimise thermal photon leakage and improve system fidelity.
Chris Mueth, Senior Director for New Markets at Keysight, said: “Quantum System Analysis marks the completion of a truly unified quantum design workflow, seamlessly connecting electromagnetic and circuit-level modelling with comprehensive system-level simulation. By bridging these domains, it eliminates the need for fragmented toolchains and repeated cryogenic testing, enabling faster innovation and greater confidence in quantum system development.”
Mohamed Hassan, Quantum Solutions Planning Lead at Keysight, said: “Quantum System Analysis is a leap forward in accelerating quantum innovation. By shifting left with simulation, we reduce the need for repeated cryogenic experiments and empower researchers to validate system-level designs earlier in the development cycle.”
Quantum System Analysis is available as part of Keysight’s Advanced Design System (ADS) 2026 platform and complements existing quantum EDA solutions. It supports superconducting qubit platforms and is extensible to other modalities such as spin qubits, making it a versatile choice for quantum R&D teams.