Adding flexibility to IoT system development
John Jones, Director of Innovation at Avnet Silica, discusses some of the challenges and choices in developing systems and applications for the Internet of Things (IoT), and how the Visible Things platform can enable fast and easy development of secure, scalable edge-to-enterprise solutions for a multitude of industrial applications.
The IoT offers a technological revolution that can deliver higher efficiencies and enhanced productivity in existing equipment infrastructure. In addition it helps to leverage cloud-based IT technologies and capabilities that are becoming increasingly powerful. The implementation of real time data analysis can enable autonomous decision making and create the potential for new services and revenue streams for companies.
However, it can be a complicated, fragmented and potentially fraught transformation for many, especially those operating in industrial sectors. For example, the industrial world comes with decades of legacy equipment and existing infrastructure that cannot easily be replaced quickly or cost effectively. Introducing new embedded hardware and software to connect smart sensor technologies up with the cloud and enterprise software, potentially via an internet gateway in many cases, brings issues of connectivity, interoperability, security and scalability. All of which can present a serious challenge in connecting up previously unconnected systems and devices, especially when dealing with solutions from multiple vendors.
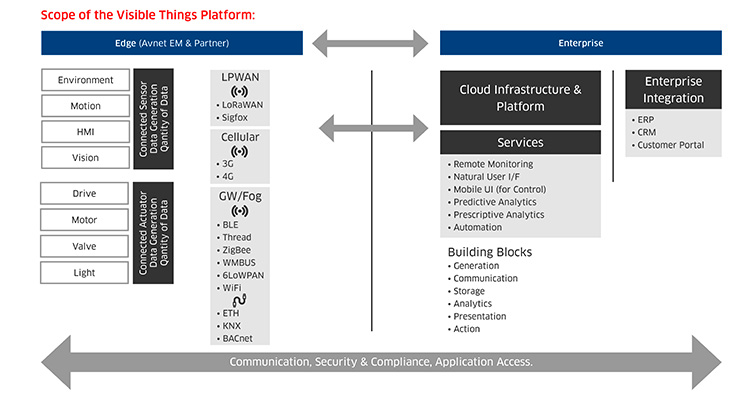
Markets and applications
Today there are widely varying estimates for the IoT market – but to choose one from many, market analyst firm IHS predicts rapid expansion over the next few years, resulting in an installed base of more than 50 billion internet connected devices by 2025 with new connected device shipments predicted to be more than 12 billion per year. A large share of the installed base is expected to be in industrial application sectors with approximately 20 billion connected devices deployed across a range of markets including industrial automation, building and home automation, smart metering and in alarm and security products and systems.
This growth is being driven by numerous new applications and capabilities. A classic IoT application is predictive maintenance, where for example manufacturing or operation data is collected via sensors located within or near to equipment and sent into the cloud for real time data analysis.
This enables the ability to accurately diagnose and prevent equipment failure, which can be a significant advantage for manufacturing companies and vital for critical service infrastructure. Predictive maintenance can provide a significant impact in high-tech manufacturing and smart factories and in what is being called the Industry 4.0 revolution in Germany.
Another key application is track and trace for transport and logistics markets. The installation of low power narrowband transmitters within vehicles or large assets, in conjunction with data analytics in the cloud, can enable the real time tracking of shipments, providing improvements in delivery as well as for insurance purposes. It can also deliver the potential to optimise logistics routes or warehouse capacity. Another example is the installation of fire alarms in homes, where the inclusion of connectivity with additional devices such as presence sensors can deliver a higher level of service as well as the potential to offer complete applications and services to end customers.
Challenges and connectivity choices
There are many challenges for companies looking to introduce IoT systems and applications. These include the low power requirements of edge devices, especially remote devices that will typically be required to operate from small batteries; scalability and the ability to manage potentially thousands or even millions of devices; the vexed issues of security; and interoperability of discrete solutions at different levels of the IoT chain.
There are also many choices to be made in terms of connectivity. Traditional possibilities involve short range wireless communications usually wireless LAN, Bluetooth Smart (Low Energy profile) or ZigBee from edge devices to a gateway, often wired via Ethernet to the cloud or potentially connected via wireless LAN. Another option is cellular connectivity from the gateway or even from edge devices to send data directly into the cloud, but this brings the penalty of high power messaging that is not always suited to the small size information packets typically required for IoT data.
However, there exist alternative connectivity options with low power narrowband messaging provided by LPWAN (Low-Power Wide-Area) network technologies such as LoRaWAN and SIGFOX. Complementing cellular mobile network and short range wireless, the fundamental concept for LoRaWAN and SIGFOX is that many IoT and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) edge devices will only need to transmit small amounts of data as well as operating from a small battery. These LPWA technologies enable significantly lower costs and better power consumption characteristics as well as supporting large networks that have many millions of battery powered edge devices. LoRa offers data rates from 0.3 up to 22kbps, whereas SIGFOX employs UMB (UltraNarrowBand) technology, which makes it well suited to even smaller data sizes, delivering from 10bps up to 1,000bps.
Typical consumption of a SIGFOX modem for example is between 20 and 70mA and is virtually zero when inactive. This level can enable battery life of years for edge devices, especially with occasional rather than continuous transmission demands. Today, however, network coverage is limited to an extent with SIGFOX networks, for example, being rolled-out in major cities, but largely within western Europe including Benelux, France, Portugal, Spain and the UK.
In addition, there is also a new and emerging LPWA standard - NB-IoT (NarrowBand IoT), which is backed by major telecom operators and equipment vendors worldwide. The technology is part of the GSMA’s Mobile IoT Initiative to deliver low cost and low power communication for IoT networks using cellular standards. Today, the initiative is perhaps still in its nascent phase, but it offers much promise.
Visible things
To help companies looking to take advantage of the possibilities offered by the IoT, Avnet Silica has put together all the building blocks necessary to deliver a flexible edge-to-enterprise evaluation and development IoT platform. Targeting a wide range of markets, the Visible Things platform is one of the first IoT systems and application platforms to be made available from an electronics component and systems distributor. The platform delivers integrated hardware and embedded software to connect smart sensors and embedded devices via gateway solutions or LPWA networking technologies, right through to the cloud and enterprise software applications. It is designed to be a highly flexible offering that provides customers a menu of different options along the path from edge to enterprise.
The platform supports short range connectivity to a gateway, and WiFi, 3G and 4G cellular communications to the cloud and enterprise software applications. It also supports the SIGFOX and LoRaWAN IoT networks, which have been designed to provide secure low cost narrowband information messaging to meet the requirements of the IoT and smart city, Machine-to-Machine and industrial applications.
A further hardware communications feature of the platform is the introduction of EUICC technology. Based on silicon-on-board technology rather than the use of standard SIM cards, the EUICC standard being driven by the GSMA enables the hosting of multiple mobile network provider profiles. Importantly, EUICC technology can be programmed Over-The-Air (OTA) to enable an application to use a specific profile or change profile at any time without the need for the physical replacement of a SIM. This can bring significant advantages for customers in the automotive or metering businesses, for example, it can enable the changing of mobile network operators easily and wirelessly during the lifecycle of an end node, which could be many years, without the requirement to change any hardware.
In terms of security, the platform offers end-to-end edge-to-enterprise or sensor-to-server security. It includes the UbiquiOS secure gateway embedded software, which integrates cryptographic technologies as well as Transport Layer Security v1.2, and server certificate (OCSP) and client certificate authentication. Additionally, the platform builds in silicon-based technologies that can integrate a secure element for deployment in smart sensor edge devices. As an example, the platform offers a gateway product that is designed for industrial applications and comes with a unique security architecture. This architecture delivers true enterprise grade security from the IP network core all the way to smart sensor configurations at the network edge, including low power non-IP-based sensors, communicating via Bluetooth for example.
Cloud services
A key element offered by the Visible Things platform is a range of cloud services. At the entry level is Devicepoint, which is a bespoke cloud software evaluation platform underpinned by IBM software components. The service builds upon data from sensors and edge devices with contextual information, plus data from other sources to deliver real time analysis and long term business intelligence. The tool can also be customised to enable greater management of sensor data for analytics, reporting and workflow management.
However, beyond this, Visible Things also supports a full open platform based on IBM Bluemix and Microsoft Windows Azure solutions. These platforms can provide industrial customers with pre-approved software evaluation environments to develop more advanced IoT applications with higher levels of flexibility and scalability and, if appropriate, the potential for full scale application deployment.
The Visible Things platform is also supported by a mobile application that runs on iOS and Android devices, and provides users with easy configuration of local hardware as well as supporting connections to cloud services. The application is fully integrated and comes with a quick-start guide to make it easy to connect the system from edge to enterprise and provide a rapid proof of concept.
Starter kits
Delivering a simple out-of-the-box set-up, a wide range of reference design starter kits have been made available to enable developers to get applications up and running quickly, targeting entry level applications to home automation or even deployment in more advanced industrial environments. Each starter kit includes a board managed by ARM Cortex-based microcontrollers.
The basic Visible Things starter kit comprises a smart sensor board including Bluetooth Smart connectivity and motion, temperature/humidity and light/proximity sensors, together with a gateway board, which manages connectivity to the cloud service via WiFi. Available as an expansion option, a GSM peripheral module with embedded SIM and SIM-connector options enables cellular connectivity to cloud enterprise software services. SIGFOX and LoRaWAN based kits include SIGFOX and LoRaWAN module sensors respectively, as well as additional motion and light sensors.
A second primary Visible Things kit is a reference design starter kit that targets a wide range of industrial applications including: remote monitoring, predictive maintenance of motors and drives, room control in homes and buildings, lighting, security and surveillance, home appliances, smart energy metering and healthcare, as well as industrial automation applications such as inspection capabilities, drive monitoring and sensor hubs.
The kit is based upon the Renesas Synergy industrial microcontroller and software platform, which has been specially designed to meet the demands of industrial environments. The kit also builds in smart pressure and energy harvesting sensors, and an increased range of connectivity options well suited for industrial deployment, including CAN, NFC and industrial Ethernet, as well as PoE (Power over Ethernet). Both the gateway and sensor boards also integrate the end-to-end sensor-to-server secure-element technology especially developed for the Visible Things platform. In addition, and in conjunction with the high end processing capabilities of the Renesas Synergy microcontroller, the platform also brings advanced embedded vision capabilities with the inclusion of a high resolution camera module that is well suited for image capture applications in factory automation, for example.
Edge-to-enterprise
While the challenges and choices are many in developing IoT systems and applications, the opportunities are greater still in being able to deliver better efficiencies and new services to customers. The Visible Things platform is a flexible IoT development solution that offers tested, proven and integrated components to enable companies an exceptionally fast edge-to-enterprise IoT deployment. The platform will also be continually augmented in the future with new hardware and software options such as support for NB-IoT communications or more cloud services along with other new features and technologies as they become available.


