Software runs the modern healthcare ecosystem, from life-saving medical devices to patient record systems. With this growing digital footprint comes the rising risk of cybersecurity. That’s where the IEC 81001-5-1:2021 standard comes in, a framework developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and cybersecurity of health software and IT systems across their entire life cycle.
Why is security in medical industry so critical?
Imagine a world where hackers can easily hijack the software controlling a ventilator or breach patient data. The consequences would be devastating, from direct threats to human life to privacy violations. IEC 81001-5-1 addresses these risks by embedding cybersecurity into every stage of a health software product’s life, from design and development to deployment and eventual retirement. It’s not about patching vulnerabilities after the fact. It’s about building security from the beginning.
A deep dive into the product life cycle
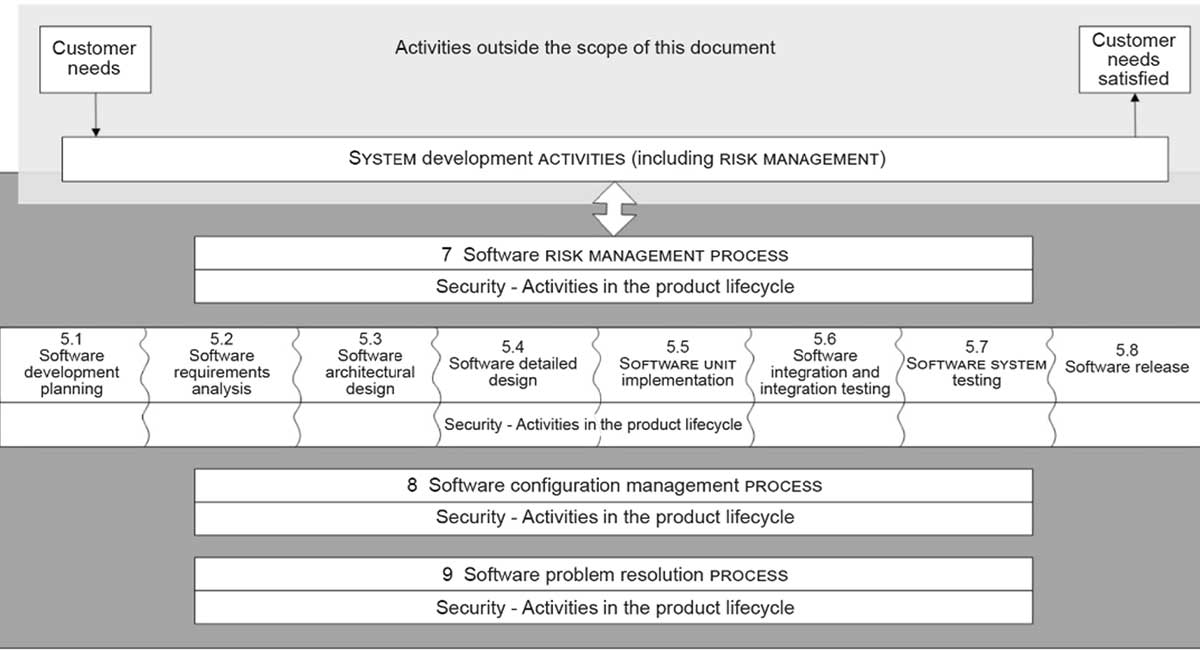
Jointly developed by the IEC and ISO, the standard promotes a life cycle model for secure development. That means considering not just the software itself, but the environment it operates in. Think of it like designing a fortress, you don’t just build walls and hope they hold. You plan layers of defense, inspect the materials, and constantly monitor for cracks. Similarly, for health software, IEC 81001-5-1 outlines activities that manufacturers must undertake, including:
- Quality management and risk management. Establishing robust systems to manage quality and, critically, to identify and mitigate security risks throughout the software’s journey. This includes identifying vulnerabilities, threats, and their potential impact on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of assets.
- Secure development processes. This involves everything from secure coding standards and practices to rigorous security architectural design and review. It’s about designing security from the ground up, not as an afterthought.
- Testing, testing, and more testing! Before releasing any health software, it undergoes extensive security testing, including vulnerability testing and even penetration testing, to ensure it can withstand potential threats. Independent testers play a crucial role here to avoid conflicts of interest with developers.
- Post-release activities. The security journey doesn’t end once the software is deployed. The standard emphasizes ongoing maintenance, timely delivery of security updates, and a process for addressing and disclosing security-related issues. This includes monitoring public incident reports and ensuring continuous improvement of the security development life cycle.
The ‘defense-in-depth’ strategy
One of the central ideas in IEC 81001-5-1 is ‘defense-in-depth.’ It’s not just a buzzword. It’s a practical philosophy that layers multiple security controls so that if one fails, others still stand. Like a medieval castle with moats, towers, and fortified walls, this approach drastically reduces the chances of a successful attack and limits the damage if one occurs.
How IEC 81001-5-1 turns health software into a fortress
IEC 81001-5-1 marks a shift in how security is approached, not as a late-stage checkbox, but as a continuous practice. Secure coding, threat modeling, and penetration testing aren’t optional steps, they’re baked into every phase of the life cycle. The goal is to reduce real-world cybersecurity exposure through early identification and remediation of risks.
IEC 81001-5-1 is the engine that drives security assurance from start to finish. At the foundation is security requirements testing, where teams verify that all security features behave correctly, even under stress, malformed inputs, or oddball use cases. Cloud integrations? Those get tested too, ensuring that services like SaaS and PaaS don’t become backdoors.
Next comes threat mitigation testing. Instead of assuming defenses work, developers must prove it. That means actively challenging every control, seeing if it holds up under pressure or can be bypassed, and making sure fixes don’t create new problems along the way.
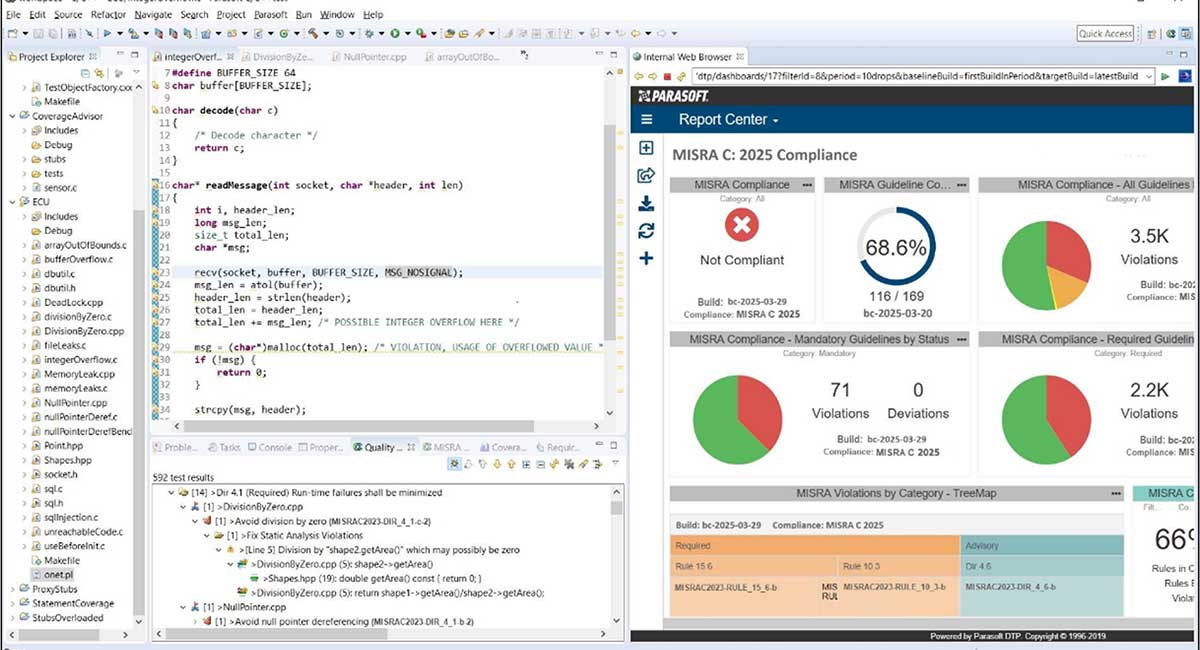
The standard also demands vulnerability testing that digs deeper than traditional QA. This includes fuzzing, abuse-case scenarios, and analyzing external interfaces and third-party components for hidden flaws. Dynamic testing uncovers runtime issues like memory leaks or insecure communications – catching what static checks might miss.
Speaking of which, static analysis takes a starring role in IEC 81001-5-1. It gives teams a fast, automated way to scan code for vulnerabilities before it ever runs. Think buffer overflows, unsafe functions, or violations of secure coding standards like MISRA or CERT. It’s all about finding flaws early and keeping your codebase clean, especially when updates or third-party libraries are involved.
Then there’s penetration testing, which raises the bar by simulating real-world attacks. Performed by independent specialists, this kind of testing adds objectivity and reveals what internal testing might miss, just like an actual attacker would.
Together, these layers of testing form a continuous shield around your software. IEC 81001-5-1 makes one thing clear: cybersecurity isn’t a finish line, it’s a loop. And testing is how you stay ahead of the threats chasing you around it.
Conclusion
In essence, IEC 81001-5-1:2021 is a blueprint for building trust and resilience. By following its guidelines, manufacturers contribute to a safer, more secure future for patients and healthcare providers.
About the author:

Ricardo Camacho, Director of Product Strategy: Embedded Safety-Critical & Compliance, Speaker & Author At Parasoft