The dawn of a new era
Wireless technology now goes far beyond cable replacement, as Joakim Lindh, Applications Manager for HID and Automotive solutions within the Bluetooth Smart business at Texas Instruments, explains.
Wireless technology, with its multiple purposes and ease of use, has changed everyday actions and interactions, and is continuing to pave the way for seamlessly connected experiences. With an install base of over three billion units, Bluetooth wireless technology is nowone of the most prominent short-range communications technologies. Originally intended to replace the cables connecting portable and/or fixed devices whilst maintaining high levels of security, low power and low cost, Bluetooth has evolved to be able to simultaneously handle data and voice transmissions.
Reinventing the remote
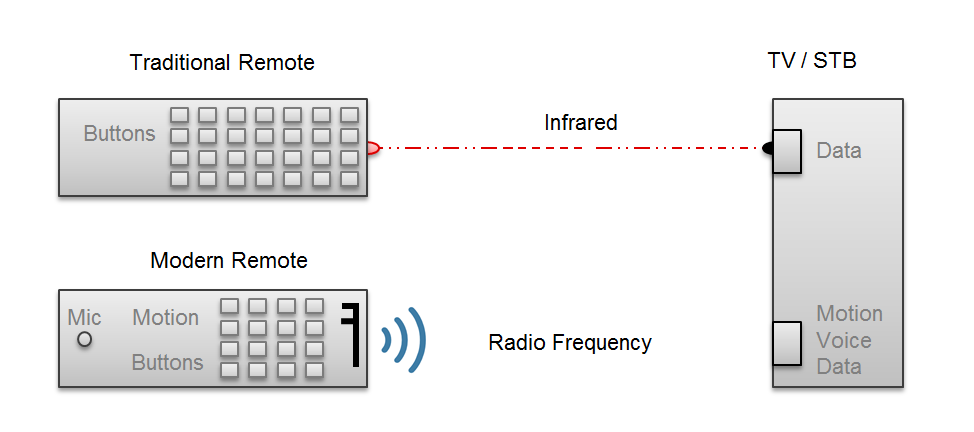
For many years, remote controls have been realised through employing infra-red (non-visible) light to transmit information over the air. However, as communication is based on light, either a direct or indirect (where the signal is ’bounced’ off or reflected by objects) line of sight is required. Today, with modern TVs and Set Top Box (STB) solutions, this is no longer required due the increasing use of RF (Radio Frequency) technology. Bluetooth has enabled this evolution of remote controls; from being simple ‘point and click’ devices to highly responsive and efficient portable controls. Replacing IR with RF technology also allows users to hide receivers behind closed cabinets or even use their remotes from another room.
RF technology can transmit and receive information simultaneously as it travels through and around objects. In wireless connectivity systems, there are several protocols that can be used to achieve low power operation and for remote controls targeting the STB and TV markets, a standardised protocol is required. While ZigBee’s RF4CE protocol is dominating the STB market, Bluetooth Classic has been popular in the TV market. But now Bluetooth Smart is marching in, taking big steps towards taking over the TV market due to its lower cost and lower power than Bluetooth Classic, and entering the STB market where a Bluetooth Smart 4.0 host is included. The benefit of using Bluetooth Smart is that most modern TVs already have a Bluetooth Smart Ready solution, which means that any Bluetooth Smart remote (or modern smartphone for that matter), could be used to change the channel.
However, changing channels is not the only common interaction nowadays. TVs and STB are being packed with apps, games and functionality that require faster and more precise input data. Some vendors already have remotes with air mouse capabilities and voice transmission. With Bluetooth Smart, the implementation is trivial with already standardised profiles (such as Human Interface Devices – HID over GATT) and with the help of a decent development kit with on board 9-axis motion tracking and digital microphone, the prototype solution is already there. The future for interactive communication lies in smart and innovative solutions. Gestures and voice commands allow new and interactive ways of interfacing to information or entertainment sources.
Bringing smart to automotive
The application of wireless communication using Bluetooth Smart also extends beyond the house. Within a car there are numerous point-to-point communication lines — side mirrors, seat heaters, tire pressure as well as key fob entry and ignition — and Bluetooth Smart can be used for all of them.
For example, a Bluetooth Smart key fob would be advertising and based on the transmitted information is recognised by the car. The car then requests an encrypted and authenticated connection to verify the key. When this is done, the car opens the door. Although a simple process in itself, consider the various ways that might trigger the advertising in the first place; a button press, voice command, or motion.
The new SimpleLink SensorTag from TI provides the necessary functionality to implement the above scenarios. The 10 on-board sensors including motion, temperature, magnet, light, pressure as well as its digital microphone are just the start of a new way of creating smart applications. There are also development plug-in modules that allow additional sensors (for example Grove Sensors) and interactive components to be interfaced for a complete solution prototype. With a full software development kit and all required tools, rapid prototyping is incredibly simple.
The new SensorTag uses the SimpleLink ultra-low power CC2650 wireless microcontroller with a 2.4GHz software configurable radio. It also supports ZigBee, 6LowPAN, RF4CE or almost any other 2.4GHz proprietary protocol.



